Magento Technical SEO is used to optimize your eCommerce website for search engines.
Some people confuse technical SEO with placing keywords strategically within quality content. But technical SEO is just as important as keywords. It involves how your Magento 2 store functions.
For example, 93% of people would leave a website if it doesn’t load quickly and 79% of customers won’t return to purchase items from a store due to slow website performance.
Without the proper Magento technical SEO structuring, you could end up losing customers and fall in rankings on Google.
To help you optimize your Magento 2 website, in this article, we will show you 11+ Magento technical SEO issues you must know and solutions to fix them.
Let’s get started!
What Is Magento Technical SEO?
Table of Contents

Technical SEO is one of the three key components of SEO (on-page SEO, technical SEO, off-page SEO).
On-page SEO is about helping search engines to understand the content of your website. Off-page SEO is about promoting your website.
And technical SEO includes all practices that are non-content elements to your website. Magento technical SEO helps search engines crawl and index your website better and enhance the user experience when people visit your website.
Technical SEO is one of the most crucial parts of your SEO strategy. It is the first step in creating a better search experience. Other SEO projects should come after you have guaranteed your website has proper usability.
Top 11+ Magento Technical SEO Issues & How To Fix Them
Now let’s look at 11+ most serious Magento technical SEO issues and learn how to fix them.
HTTPS security
Security has always been “a top priority” for Google. In 2014, Google announced HTTPS as a ranking signal and since October 2017, Google shows a “Not secure” caution sign in Chrome every time a user lands on an HTTP site.
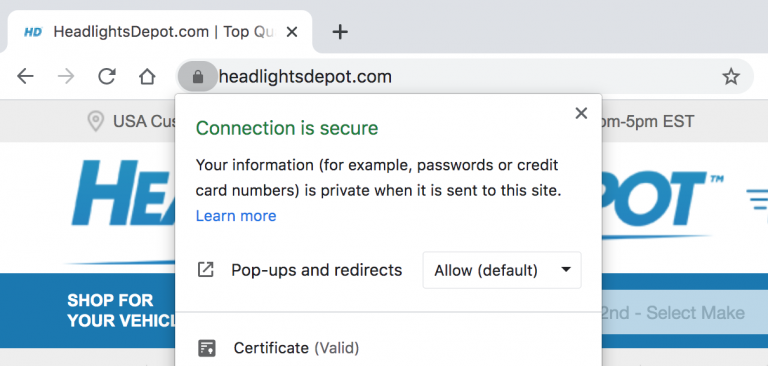
How to check?
- Type your domain name into Google Chrome. If you see a lock sign next to your website address then your site is secure. If not, then your website is “not secure” to Google.
How to fix?
- To convert your website to HTTPS, you need to purchase an SSL certificate from a Certificate Authority.
Website isn’t indexed correctly
When you search for your business name in Google, does your website show up in the top search results?
If the answer is no, then there might be an issue with your indexation. As far as Google is concerned, if your page isn’t indexed, it doesn’t exist and certainly won’t be found on the search engines.
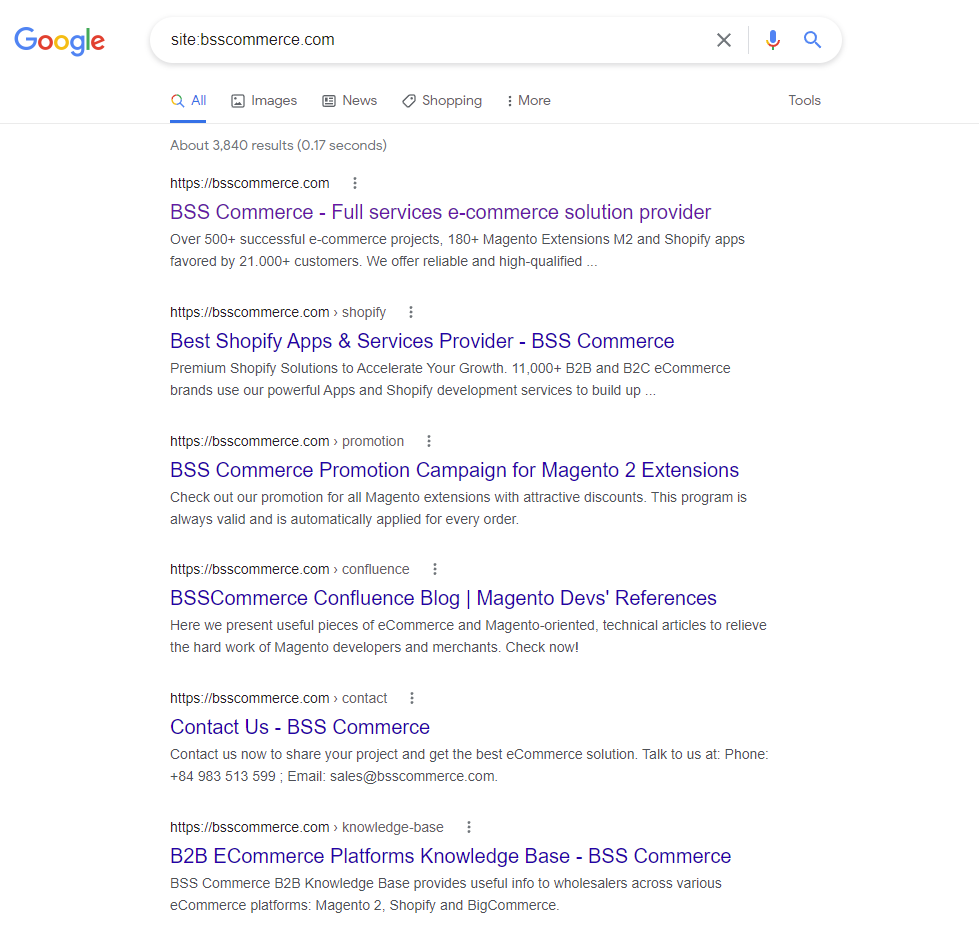
How to check?
- Type into Google’s search bar “site:yoursitename.com” and instantly view the count of indexed pages for your website.
How to fix?
- First of all, you can add your URL to Google.
- Your website is indexed, but there are many MORE results than expected, look deeper for either site-hacking spam or old versions of the site that are indexed instead of appropriate redirects in place to point to your updated site.
- In case your website is indexed, but you see LESS results than expected, perform an audit of the indexed content and compare it against which pages you want to rank. If you’re not sure why the content isn’t ranking, check Google’s Webmaster Guidelines to ensure your content is compliant.
- If the results are different than you expected in any way, verify that your important website pages are not blocked by your robots.txt file. You should also verify you haven’t mistakenly implemented a NOINDEX meta tag.
No XML sitemaps
XML sitemaps help Google bots understand more about your pages, so they can effectively and intelligently crawl your website.
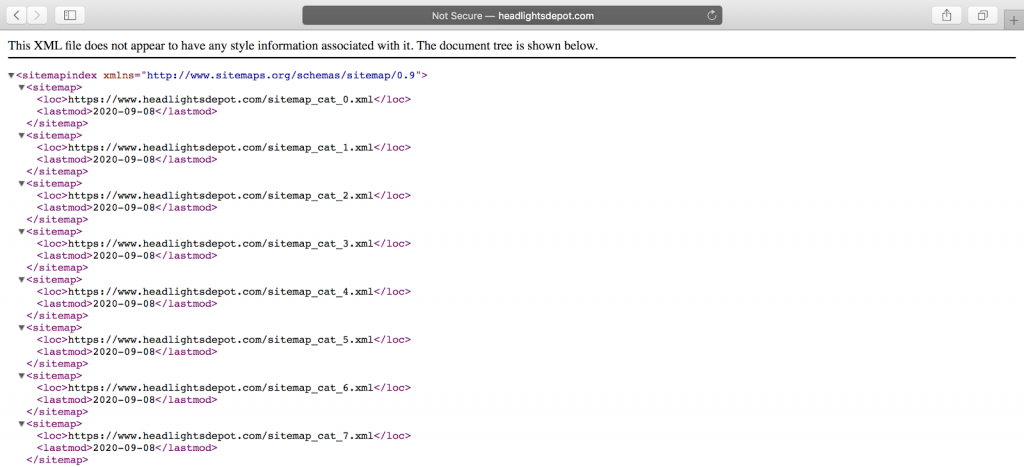
How to check?
- Type your domain name into Google and add “/sitemap.xml” to the end. If your website has a sitemap, you will see something like the following picture:
How to fix?
- If your website doesn’t have a sitemap, you can create one yourself or hire a web developer to create one for you. The easiest way is to use an XML sitemap generating tool.
Missing or incorrect robots.txt
Missing robots.txt file is a big red flag, but did you know that an improperly configured robots.txt file also destroys your organic website traffic?
How to check?
- To determine if your robots.txt file is incorrect, type your URL into your browser with a “/robots.txt” suffix.
- If you get a result that reads “User-agent: * Disallow: /” then you have an issue.

How to fix?
- If you see “Disallow: /”, talk to your developer.
- If you have a complex robots.txt file, like many eCommerce sites, you should review it line-by-line with your web developer to make sure it’s correct.
Meta robots NOINDEX
NOINDEX can be even more damaging than a misconfigured robots.txt.
Most commonly, the NOINDEX is set up when a website is in its development phase, but once the website goes live, it is imperative to remove the NOINDEX tag.
Since so many web development projects are running behind schedule and pushed to live at the last hour, this is where the mistake can happen. Do not blindly trust that it was removed, as the results will destroy your site’s search engine visibility.
When the NOINDEX tag is appropriately configured, it signifies certain pages are of lesser importance to search bots. However, when configured incorrectly, NOINDEX can immensely damage your search visibility by removing all pages with a specific configuration from Google’s index.
How to check?
- Right-click on your site’s main pages, select View Page Source, then manually do a spot-check by viewing the source code of your page (.”), see if there is any line that read “NOINDEX” or “NOFOLLOW”.

How to fix?
- If you see any “NOINDEX” or “NOFOLLOW” in your source code, check with your developer if they have included it for specific reasons.
- If there is no reason, have your developer change it to read <meta name=”robots” content=” INDEX, FOLLOW”> or remove the tag altogether.
Multiple home URL versions
Every website should have the following two properties setup in Search Console:
- https://www.yourwebsite.com
- https://yourwebsite.com
Users usually don’t care if your home page shows up as all of these separately, but the search engines do.
If Search Console is successfully set up for your website, you should only see one of the website versions getting all the attention.
Setting the preferred website version in Google Search Console is a good first step in addressing the numerous versions of your website, but it is more than just selecting how you want Google to index your website. Your preferred website version affects every reference of your website’s URL, both on and off the site.
How to check?
- Check manually if different versions of your URL successfully flow to one standard URL.
How to fix?
- If you discover multiple indexed versions, you will need to set up 301 redirects or have your web developer set them up for you.
Incorrect rel=canonical
Rel=canonical is particularly important for all websites with duplicate or very similar content (especially eCommerce websites).
Dynamically rendered pages (like a category page, product page or blog post) can look like duplicate content to Google search bots. The rel=canonical tag tells search engines which “original” page is of primary importance (hence: canonical) and similar to URL canonicalization.
How to check?
- Spot-check important pages to see if they’re using the rel=canonical tag.
- Use a website scanning software to list out all the URLs on your website and determine if there are duplicate page problems that can be solved with a rel=canonical tag.

Duplicate content
With more and more brands using dynamically created websites, content management systems, and practicing global SEO, the problem of duplicate content plagues many websites.
The problem with duplicate content is that it may “confuse” search engine crawlers and prevent the correct content from being served to your target audience.
How to check?
- You can use tools like CopyScape and Siteliner to find duplicate content.
How to fix?
- Add proper Rel=Canonical.
- Use and proper configuration.
- Correct implementation of hreflang tags
Not enough use of structured data
Google defines structured data as: “a standardized format for providing information about a page and classifying the page content…”
Structured data is a simple way to help Google search crawlers understand the content and data on a page. For example, if your page contains a recipe, an ingredient list would be an ideal type of content to feature in a structured data format. Address information like this example from Google is another type of data perfect for a structured data format.
How to check?
- Use the Rich Results Tool, created by Google to help you validate and test the syntactic correctness and alignment to Google recommendations of your schema markup.
How to fix?
- As you roll-out new content, identify opportunities to include structured data on the page, and coordinate the process between content creators and your SEO team. Better use of structured data may help improve CTR and possibly improve rank position in the SERP. Once you implement structured data, review your Google Search Console report regularly to make sure that Google is not reporting any issue with your structured data markup.
Broken links
Good internal and external links show both users and search crawlers that you have high-quality content. Over time, content changes, and once-great links break. Broken links create a poor user experience and reflect lower-quality content, a factor that can affect page ranking.
A website migration or relaunch project can spew out countless broken backlinks from other websites. Some of the top pages on your site may have become 404 pages after a migration.
How to check?
- You can use tools like Google Search Console, Moz, Majestic, or Ahrefs to find all external links that are broken.

How to fix?
- After identifying links that are broken, 301 redirect these to the best pages.
Slow page speed
If your website doesn’t load quickly, your users will go to another page. Site speed matters to the user experience and to Google.
How to check?
- Use Google PageSpeed Insights to detect specific speed problems with your website.
How to fix?
- Common website speed solutions include image optimization/compression, server response time improvement, browser caching improvement and JavaScript minifying.
LEARN MORE: Tips to optimize Magento 2 Core Web Vitals for better SEO rankings!
Mobile device optimization
You need to ensure your website is mobile-friendly for exceptional mobile user experience.
How to check?
- Open your website on mobile devices to see if there is any problem.
How to fix?
- Guarantee the appropriate and correct hreflang code and links.
- Update all meta-data on your mobile site.
- Add structured data to your mobile pages and make sure the URLs are updated to mobile URLs.
The Best Solution To Optimize Magento Technical SEO
Hereby, we want to introduce you to the best solution to optimize your overall SEO:
Magento 2 SEO Extension by BSS

This toolkit provides every single function that you should add to your website for better SEO: rich snippets, sitemap, index, duplicate content, 3010 redirects, meta template, image alt tag, SEO external links and SEO report.
With the help of this module, top 1 Google will be within your reach.
Conclusion
In this article, we have shown you 11+ Magento technical SEO crucial issues and the best solutions to fix them.
We hope this blog is helpful and good luck to you!
BSS Commerce is one of the leading Magento extension providers and web development services in the world. With experienced and certified Magento developers, we commit to bringing high-quality products and services to optimize your business effectively. Furthermore, we offer FREE Installation – FREE 1-year Support and FREE Lifetime Update for every Magento extension.
CONTACT NOW to let us know your problems. We are willing to support you every time.

